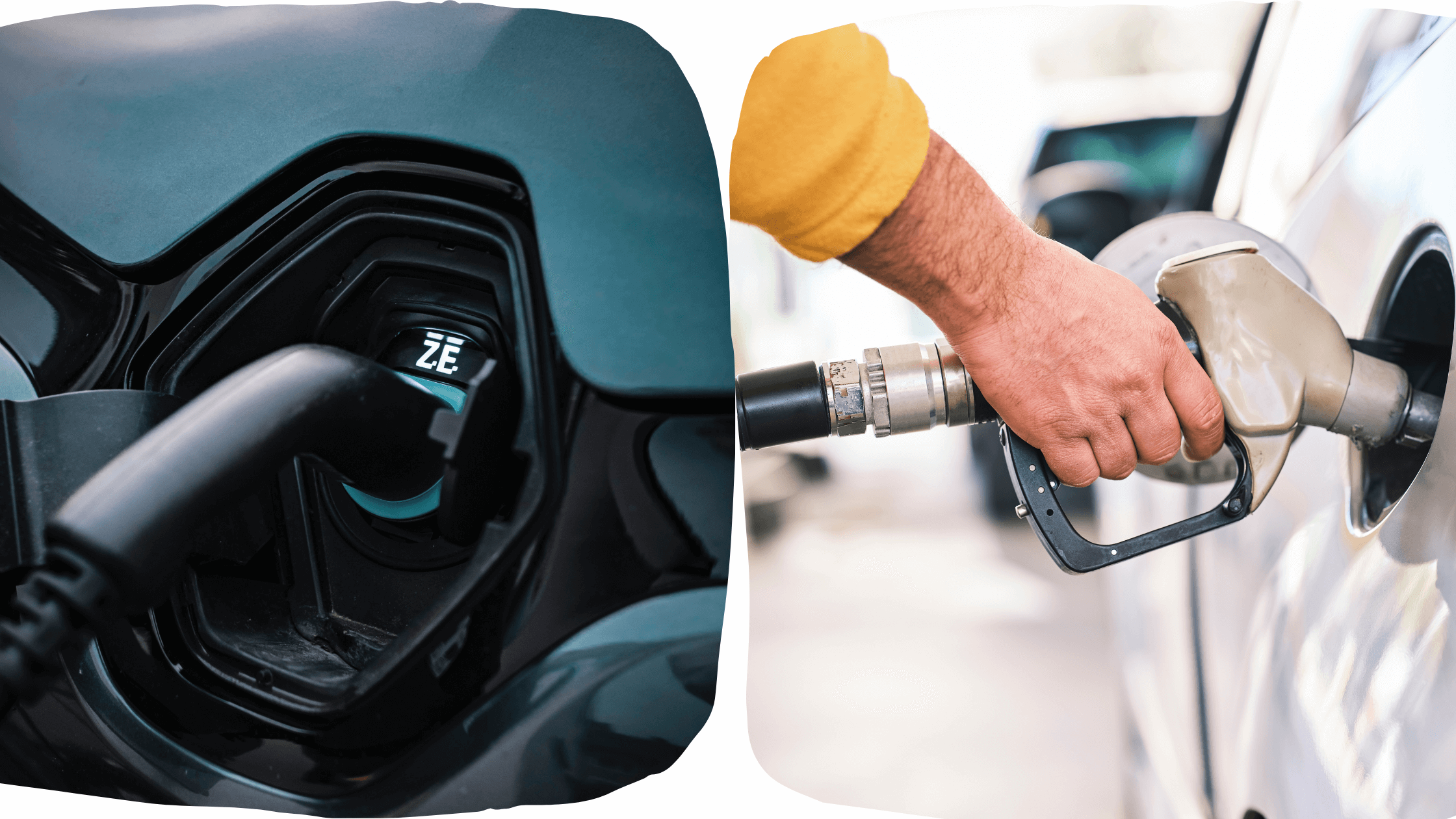
Electric cars and gas-powered cars are two types of vehicles that have been on the market for many years.
Both serve the purpose of transportation, but they differ significantly in functionality. Electric cars use electricity stored in batteries, while gas-powered cars rely on gasoline as fuel.
This article outlines the five key differences between electric and gas-powered cars.
Gas cars need refueling at gas stations. In contrast, electric cars can be charged at home or public charging stations.
The second difference is fuel cost. Gasoline prices can be unpredictable, while electricity prices are generally more stable.
Also, electric cars are more fuel-efficient, allowing them to travel further on a single charge compared to gas-powered cars on a tank of gas.
Table of Contents
Powertrain Mechanics
Electric Motor Functionality
Electric cars run on an electric motor converting electrical energy to mechanical energy. The motor is powered by a battery pack that stores the electrical energy and delivers it to the motor.
The motor then uses this energy to rotate the wheels of the vehicle. Electric cars ditch the traditional transmission and clutch, opting for a single-speed system to transfer power to the wheels.
Internal Combustion Engine Basics
The engine is connected to a transmission that transfers the power to the wheels. And transmission has several gears, allowing the engine to work efficiently at different speeds. So driver can select the appropriate gear for the speed and driving conditions.
The ICE works by compressing a mixture of air and fuel in a cylinder and igniting it with a spark. The resulting explosion pushes a piston, which turns a crankshaft, and ultimately rotates the wheels. The process repeats for each cylinder in the engine, which can have anywhere from four to twelve cylinders. The exhaust gases are then expelled from the engine through the exhaust system.
Energy Sources and Efficiency

Electricity Storage and Consumption
A key distinction between electric and gas cars is their energy source.
Electric cars use stored electricity in batteries, while gas cars rely on gasoline. The efficiency of storing and using electricity is vital for electric car performance.
Electric cars use lithium-ion batteries to store a substantial amount of energy, powering the car’s motor.
But, the limited energy storage in batteries impacts the car’s range.
Fuel Types and Combustion Efficiency
Gas-powered cars, on the other hand, use gasoline as their fuel source.
Gasoline is a fossil fuel that is refined from crude oil. Gasoline combustion in the engine of a car produces energy that is used to power the car’s motor.
But, gasoline combustion is not very efficient, and a significant amount of energy is lost as heat.
This inefficiency contributes to the environmental impact of gas-powered cars, as it results in the emission of harmful pollutants.
Electric cars are usually more energy-efficient than gas-powered ones.
Electric motors convert more battery-stored energy into motion, while gas engines waste a significant portion of combustion-produced energy. This translates to electric cars covering more distance on one charge compared to gas-powered cars on a tank of gas.
Moreover, electric cars generate zero emissions, making them an environmentally friendly choice.
Environmental Impact
Why are electric cars greener than gas cars? Two key differences:

Emissions and Air Quality
Electric cars emit zero pollutants, keeping the air clean. In contrast, gas cars release harmful pollutants like carbon monoxide, nitrogen oxides, and particulate matter, impacting air quality and health.
Sustainability of Energy Sources
Another crucial difference between electric and gas cars is their energy source sustainability. Gas cars depend on finite fossil fuels, contributing to climate change. In contrast, electric cars can be powered by sustainable sources like solar, wind, and hydropower.
It’s important to consider that the sustainability of electric cars depends on their power sources. If an electric car is charged using electricity from a coal-fired plant, its environmental impact will be higher than using solar or wind power.
Cost of Ownership
Electric cars are often thought to be pricier than gas cars, but when it comes to ownership costs, electric cars have some notable advantages.
Let’s break down the key differences in costs between electric and gas cars.
Initial Purchase Price
Electric cars tend to have a higher initial purchase price than gas-powered cars. However, the price difference is decreasing as electric cars become more mainstream.
According to Kelley Blue Book, the average transaction price for an electric vehicle in April 2021 was $51,532. In comparison, the average transaction price for a gas-powered car was $40,857. While electric cars may have a higher upfront cost, they can save money in the long run.
Maintenance and Operating Costs
Electric cars have lower maintenance costs than gas-powered cars because they have fewer moving parts.
Electric cars don’t require oil changes, transmission fluid changes, or spark plug replacements. Instead, electric cars require routine maintenance such as tire rotations and brake pad replacements.
In fact , the average cost to run an EV in the United States is $485 per year, while the average for a gasoline-powered vehicle is $1,117.
The exact price difference depends on the gas and electric rates where you live and the type of car you drive.
In addition to lower maintenance costs, electric cars have lower operating costs than gas-powered cars.
According to a study from the U.S. Department of Energy, the total cost of traditional gas compared to an EV is about 4 cents per mile, and this includes services such as oil changes, new spark plugs, and air filters. In comparison, the cost of electricity to power an EV is about 1 cent per mile. This means that electric cars can save drivers money in the long run, even if they have a higher upfront cost.
Performance and Driving Experience

When it comes to driving experience, electric cars offer a unique experience compared to gas-powered cars. Here are some differences between the two:
Acceleration and Torque
Electric cars accelerate quickly due to instant torque, allowing them to reach 60 mph faster than gas cars.
Electric motors deliver full torque instantly, unlike gas engines that need time to build speed.
For instance, the Tesla Model S Plaid achieves 0 to 60 mph in under 2 seconds, ranking among the world’s fastest cars. In contrast, gas cars may take several seconds to hit their top speed.
Noise and Vibration
Electric cars are much quieter than gas-powered cars. This is because they don’t have an internal combustion engine, which produces a lot of noise and vibration. Instead, electric cars use electric motors, which are much quieter and smoother.
This makes for a more comfortable and relaxing driving experience. In addition, electric cars don’t produce any emissions, which means they are better for the environment and for people’s health.